What is the strategic sport communication model?
This is an excerpt from Strategic Sport Communication 4th Edition With HKPropel Access by Paul M Pedersen,Pamela C Laucella,Edward (Ted) M Kian,Andrea N Geurin.
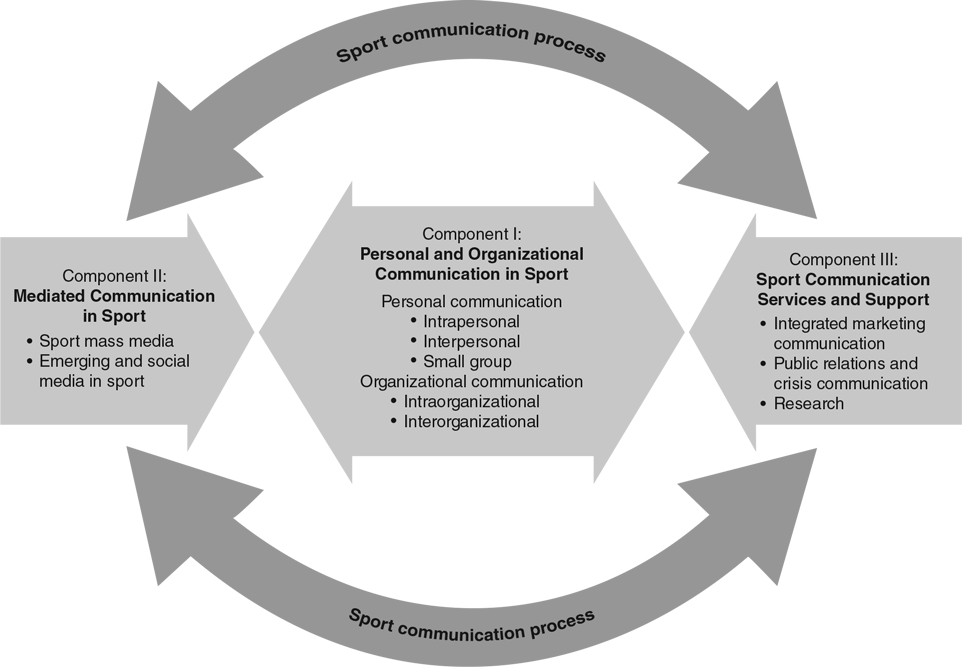
The preceding pages in this chapter lead to the formulation of a unified and dynamic model of sport communication. In our effort to represent the big picture while also detailing interrelationships between various components, we propose a conceptual analysis that presents (and integrates) both the process of sport communication and the micro and macro perspectives on the discipline. This unique model—the SSCM—illustrates the uniqueness of sport communication. It is built on the elements—theory (i.e., communication genres), context (i.e., levels and segmentation), and communication process—outlined in the preceding parts of the chapter. As revealed in figure 5.4, the SSCM explains, systematically and rationally, the relationships between the key variables in sport communication. The model’s framework bridges theory and practice by combining the process of sport communication and the main elements (categories) of the field. Therefore, it is both a process-based and a structurally based approach.
The SSCM encompasses—and is highly influenced by—the many areas and perspectives associated with communication, as well as other sport-related segments of the communication field, such as marketing and management. For example, the major influence from marketing is segmentation. By segmenting sport communication, the model includes all the major levels, contexts, and content areas of the field (e.g., advertising, broadcasting, communication studies, communication technology, social media, journalism, public relations). The context or levels of sport communication consist of three components. Component 1 includes personal and organizational communication in sport, component 2 includes mediated communication in sport, and component 3 includes sport communication services and support systems.
The major influence on the model from the field of communication consists of the processes used in communication, including sport communication. The SSCM, which uses modeling to illustrate both the process and the components of sport communication, is also influenced by the areas of applied communication (e.g., communication needs of sport organizations, ways to improve communication between sport supervisors and employees); public address, speech education, and communication education (e.g., speech, pedagogy); communication theory (e.g., analyses of communication in social interactions); gender and communication (e.g., differences and similarities in styles and characteristics); international communication; intercultural communication; legal communication; performance communication; political communication; and a host of other communication perspectives.
In short, the SSCM requires the perspectives of a variety of academic disciplines. One must understand communication theory and the process of communication to look at the entire field of sport communication. In all facets of sport communication, the communication process is evident. Sport communication is a process, and that process does not take place in a vacuum—it must be played out in a context. That context, or level, can involve personal settings (e.g., face to face, small group), organizational settings (e.g., between two sport organizations), mediated sport communication (e.g., social media postings and X posts), or sport communication support services (e.g., sport public relations podcasts). Beyond the process, the other components of the model provide a comprehensive segmentation of the entire field of sport communication. In other words, the process and components included in the model account for every activity and career, as well as every attribute and aspect, of sport communication. In this way, the model combines the process view with structural analysis of sport entities.
SHOP

Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers.
JOIN NOW
Latest Posts
- How do I integrate nutrition education into PE?
- How does the support of friends and family influence physical activity?
- What makes the Physical Best approach unique?
- Strength training gimmicks . . . or not?
- How do vitamins and minerals support our bodies?
- Why do many people have difficulty losing weight?


