Engaging fans through social media
This is an excerpt from International Sport Management 2nd Edition by Eric MacIntosh,Gonzalo Bravo,Ming Li.
By Michael L. Naraine, PhD, and Adam J. Karg, PhD
Engagement consists of three interrelated dimensions (Brodie et al., 2011, 2013) in which consumers' cognition, emotions, and behaviors are antecedents for a series of positive outcomes for brands, organizations, and events. Related to consumers, engagement sits within an expanded relationship approach to marketing (Vivek et al., 2012) in which consumers are part of interactive relationships with brands, organizations, and each other. Engagement seeks to describe relationships that extend cognition and “encompasses a proactive, interactive customer relationship with a specific engagement object (e.g., a sport brand)” (Brodie et al., 2011, p. 257). Social media and fantasy sport provide examples of digital tools that help harness and develop such relationship using digital engagement tools.
Sport provides a valuable context to explore and observe engagement given inherent aspects that are emotional, cognitive, and behavioral in nature. Sport is often described as a high-involvement service domain, in which part of the role of sport marketers is to leverage commitment and loyalty toward brands using a range of experiences, tools, and exchanges. Therefore, structuring activities to enhance emotional, psychological, and physical investment in brands is a powerful strategy for sport organizations.
The process of engagement suggests that consumers are motivated by hedonic or utility means to engage in an activity (figure 21.1). From here, a subprocess of engagement that involves sharing, socializing, codeveloping, advocating, and learning is said to develop deeper attitudes, connections, and ultimately relationships within and between consumers and organizations. This chapter will show how both social media and fantasy sport provide ample opportunities to utilize such a subprocess given the design of the tools and exchanges within them.
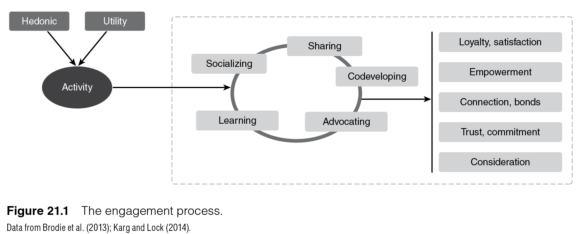
Consumer engagementprocesses, as well as antecedents and consequences, can help in developing and strengthening interactive relationships. The construct in nonlocalized or international consumer settings has much to offer, in particular when combined with tools such as social media and fantasy sport that are digitalized in nature and available for use at limited additional costs to sport organizations, leagues and events. The chapter seeks to present how these tools have developed and how they can be used to engage fans outside the traditional settings such as match or game attendance. By using digital tools that do not limit consumption to geographic boundaries, sport marketers can seek to develop engagement of fans through digital channels and leverage higher and more developed levels of interaction and consumption between organizations and consumers, and between groups of consumers. In the remaining parts of the chapter, we consider social media and fantasy sport as two such mechanisms, which are widely used in sport to development and leverage engagement.
SHOP

Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers.
JOIN NOW
Latest Posts
- Strength training gimmicks . . . or not?
- How do vitamins and minerals support our bodies?
- Why do many people have difficulty losing weight?
- How do hormones affect muscles?
- Machine learning: The cornerstone of data-driven decision making for sport organizations
- Examples of how systematic reviews and meta-analyses are used in sport


