Do Highly Cushioned Shoes Improve Running Performance?
This is an excerpt from Physiology of Sport and Exercise 9th Edition With HKPropel Access by W Larry Kenney,Jack H Wilmore,David L Costill.
Research Perspective 5.2
Running economy is critical to long-distance running performance. It is so important that it can differentiate performance between runners with a similar VO2max. In addition to substantial vertical loading forces that an athlete is subjected to while running, a combination of eccentric and isometric contractions and elastic energy storage in tendons is required to slow the downward acceleration during the initial stance phase of the gait cycle. In fact, to cover the distance of a marathon (42 km), a runner with a stride length of 2.4 m (7.9 ft) will strike the ground a total of 35,163 times! This necessarily results in the accumulation of tremendous impact load and a high volume of eccentric and isometric contractions. These effects are even more pronounced during downhill running, which is well known to result in significant muscle damage. Although it has been established that running shoes with highly compliant and resilient foam can improve running economy, it is less clear whether these beneficial effects remain evident in the presence of muscle damage.
To address this question, Black and colleagues (2022) designed a study to test the hypothesis that a highly cushioned running shoe (HCS) would (1) improve incremental treadmill test performance and running economy during exercise in a fresh, nondamaged state and (2) attenuate the deterioration in running economy elicited by downhill running–induced muscle damage. Experiment 1 used a crossover design: 32 male and female participants completed an incremental treadmill test in both the HCS and a control running shoe (CON) on separate days to determine running economy, running speed, and running time. Experiment 2 used a parallel group design in which the same participants were pair-matched to either an HCS or a CON shoe group and then underwent a single assessment of running economy both before and 48 h after a downhill run designed to elicit substantial muscle damage.
Confirming the original hypotheses, the results of experiment 1 demonstrated that an HCS improved incremental treadmill test performance by ~5.7% (without any effect on VO2peak) and reduced the oxygen cost of running by ~3.2% (i.e., improved running economy; see figure). Similarly, experiment 2 showed that after muscle damage, the oxygen cost of running was likewise lower by ~4.7% in an HCS compared with a CON (see figure)—this translates to approximately a 9 min improvement in marathon running times. Taken together, these data suggest that an HCS improves running performance and running economy both in the presence and absence of muscle damage. The results of this study have significant implications for coaches and athletes developing training programs and returning to competition after intense training or muscle injury.
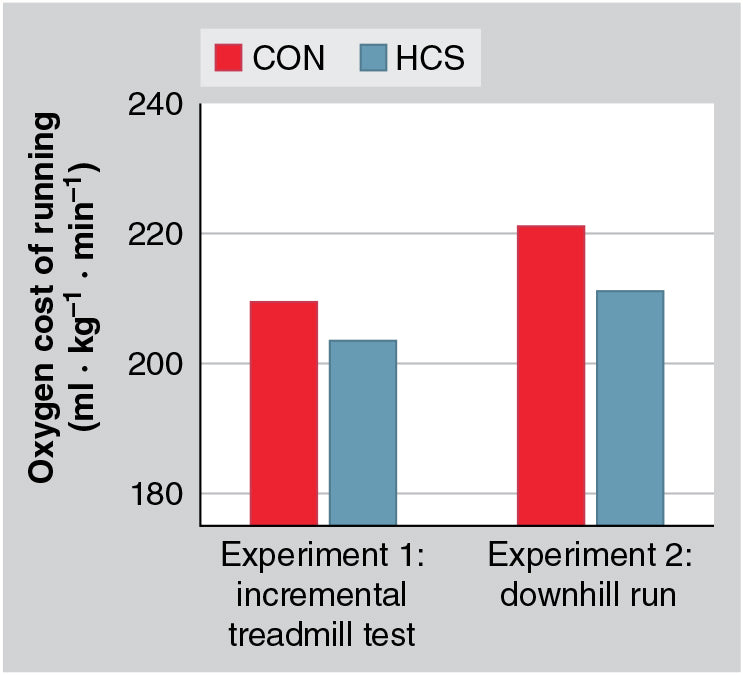
Data from Black et al. (2022).
Black, M.I., Kranen, S.H., Kadach, S., et al. (2022). Highly cushioned shoes improve running performance in both the absence and presence of muscle damage. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 54(4), 633-645.
More Excerpts From Physiology of Sport and Exercise 9th Edition With HKPropel AccessSHOP

Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers.
JOIN NOW
Latest Posts
- Sample mental health lesson plan of a skills-based approach
- Sample assessment worksheet for the skill of accessing valid and reliable resources
- Help your students overcome what holds them back from making health-promoting choices
- Example of an off-season microcycle
- Modifying lifts
- Screening for multilevel programs in a team environment


